SITUATION:
This QuickHit was developed to promote safety when using pre-filled heparin syringes, as a substitute for multi-dose heparin vials, to draw up and dilute heparin for locking of central venous access devices (CVADs) in home and community.
BACKGROUND:
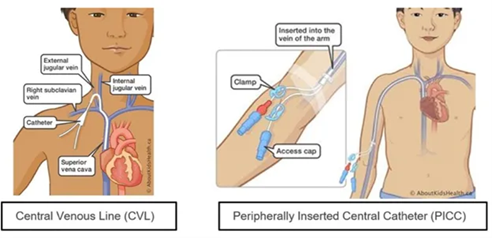
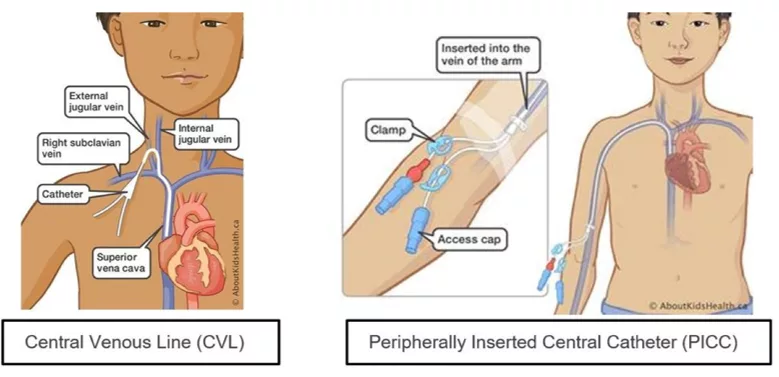
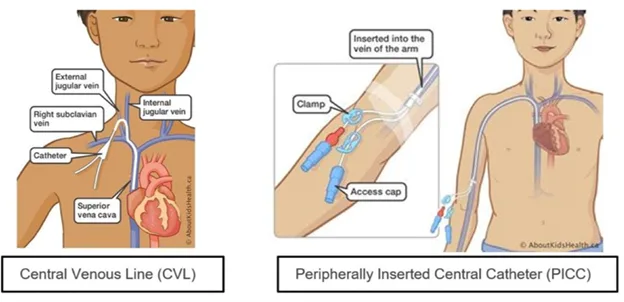
Children with medical complexity rely on CVADs in home and community care for long term intravenous therapy including medication administration, parenteral nutrition, dialysis, hydration and blood sampling. Types of CVADs include central venous lines (CVL) and peripherally inserted central catheters (PICC). Both types of CVADs may have single or multiple lumens.
Heparin locking is a procedure that helps maintain catheter patency by preventing blood from clotting in the CVAD and causing a blockage when it is not in use. The dose, concentration and volume of heparin that is ordered for heparin locking is determined by the child’s weight and the type of CVAD.
Some children require heparin doses that are diluted with normal saline prior to administration. Typically, multi-dose heparin vials (100 units/mL) are used to draw up the ordered heparin dose before dilution with normal saline. In some cases, pre-filled heparin syringes (100 units/mL) may be used as a substitute for multi-dose heparin vials (e.g., due to supply chain issues).
ASSESSMENT:
The dose of heparin required for locking a CVAD will be prescribed by the child’s healthcare provider. Heparin is typically supplied at a concentration of 100 units/mL, administered daily when a CVAD is not in use and the total volume to be administered in each lumen is 1 mL. For children that weigh more than 10 kg, a standard heparin dose of 100 units is prescribed, corresponding to 1 mL. For children that weigh less than 10 kg, a diluted dose of heparin is typically required, calculated at 10 units/kg.
Please note that children with active hemodialysis/apheresis CVADs may be prescribed high-dose heparin with a concentration of 1000 units/mL and the lumen volume and locking frequency may vary.
For example, if a child weighs 7 kg then their dose of heparin is 70 units. The dose will be drawn up as follows:
- 0.7 mL of heparin (100 units/mL)
- 0.3 mL of normal saline
- Total volume = 1 mL
The supplies required for heparin locking depend on the number of lumens the CVAD has. The following supplies are needed for heparin locking a single lumen CVAD when the heparin dose requires dilution:
- One pre-filled 5 mL heparin syringe (100 units/mL)
- One 1 mL Luer Lock syringe
- One 5 mL Luer Lock syringe
- Two needles
- 2 pre-filled normal saline syringes (one for diluting heparin dose and one for flushing CVAD)
- Alcohol swabs
- Sharps container
RECOMMENDATION:
Connected Care recommends the following to safely draw up and dilute heparin using pre-filled syringes for heparin locking CVADs:
- Confirm the child’s orders for heparin locking and ensure that you have the appropriate supplies to draw up and administer the dose.
- Ensure that a syringe smaller than 5 mL is not used to heparin lock or flush a CVAD as the increased pressure may cause the CVAD to break.
- To draw up and dilute the heparin dose, perform the following steps:
- Confirm the concentration of the heparin in the syringe is 100 units/mL.
- Draw up the appropriate heparin dose from the pre-filled heparin syringe into a 1 mL syringe using a needle. Safely recap needle once done using the one-handed scoop method to avoid needlestick injury.
- Attach a new needle to a 5 mL syringe and draw up appropriate volume of normal saline from the pre-filled normal saline syringe. Safely recap needle once done.
- Transfer the heparin from the 1 mL syringe to the 5 mL syringe by taking the following steps:
- Remove the needle from the 5 mL syringe. Dispose needle in sharps container.
- Pull back plunger of 5 mL syringe to approximately 1 mL mark.
- Uncap the needle on the 1 mL syringe and carefully insert the needle into the 5 mL syringe to transfer the heparin. The needle can then be placed on the 5 mL to protect the tip.
- Confirm accurate dose in 5 mL syringe and remove any excess air.
- Maintain aseptic non-touch technique (ANTT) and do not re-use supplies when drawing up and administering heparin to minimize risk for central line associated blood stream infection (CLABSI). If the child has a double lumen CVAD, it is appropriate to use the same pre-filled heparin syringe to draw up the heparin doses for both lumens if ANTT is maintained.
- Contact the child’s home care provider and/or Ontario Health atHome for any issues with supplies. Consult Connected Care Live for support with the skill of heparin locking.